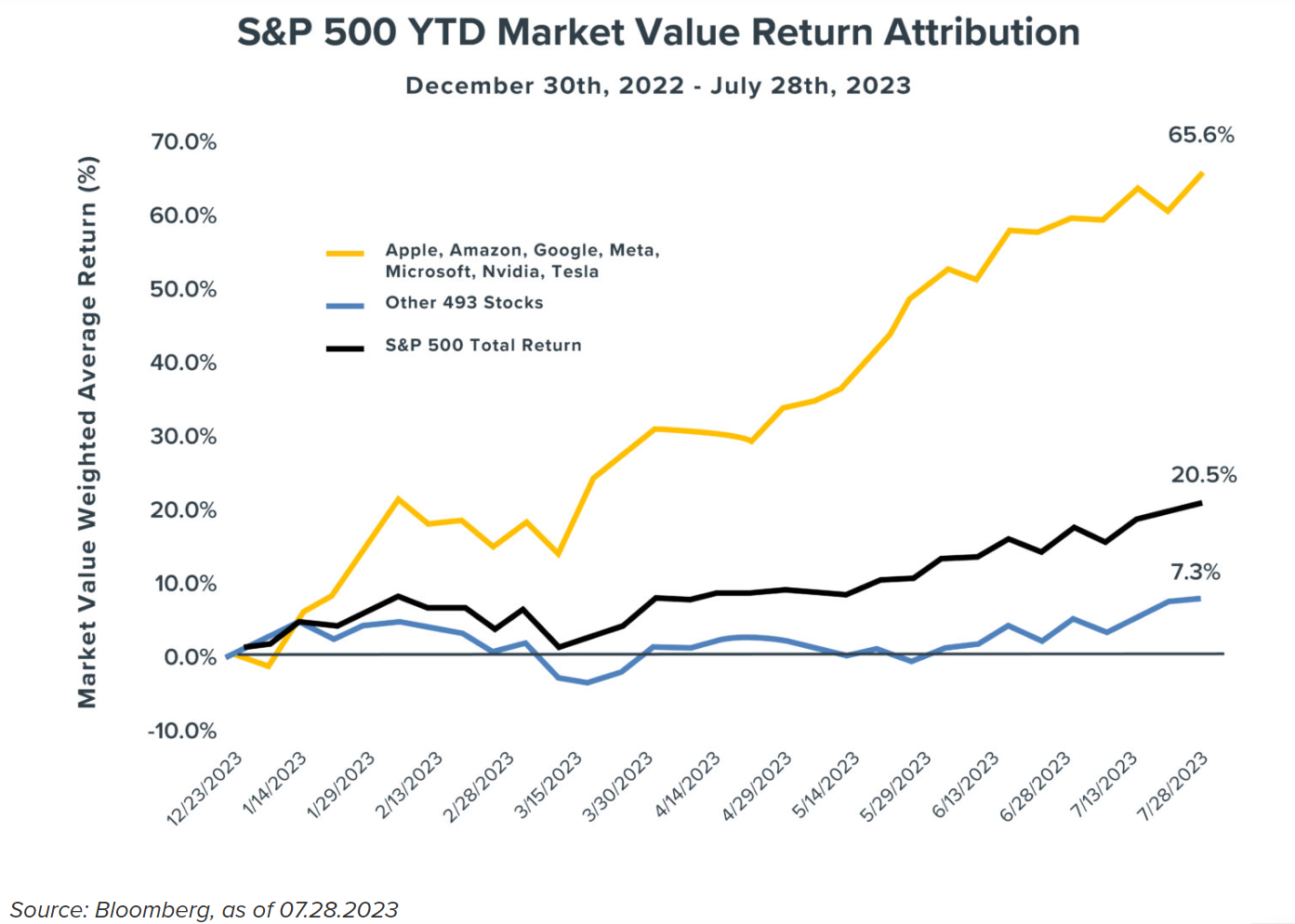
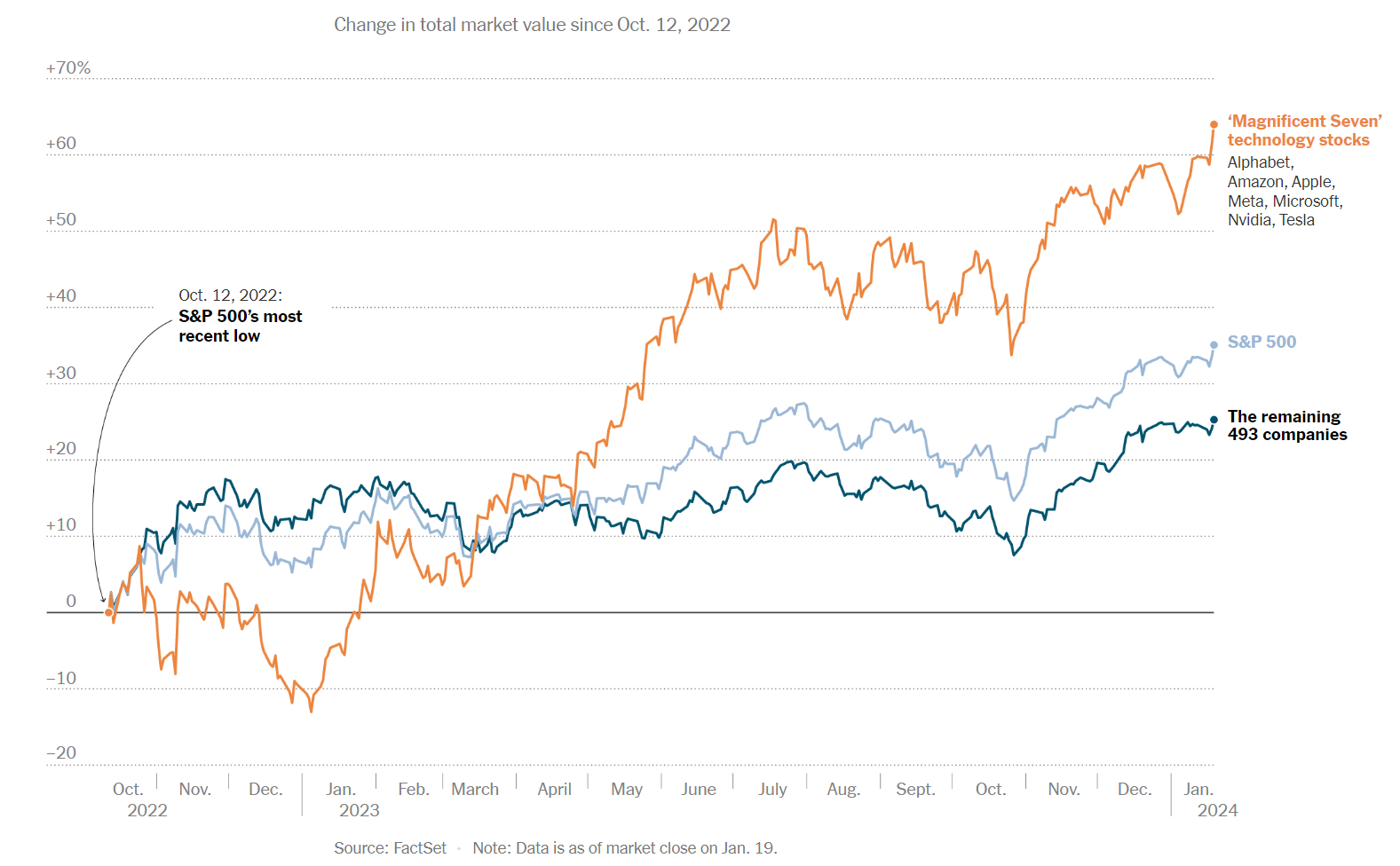
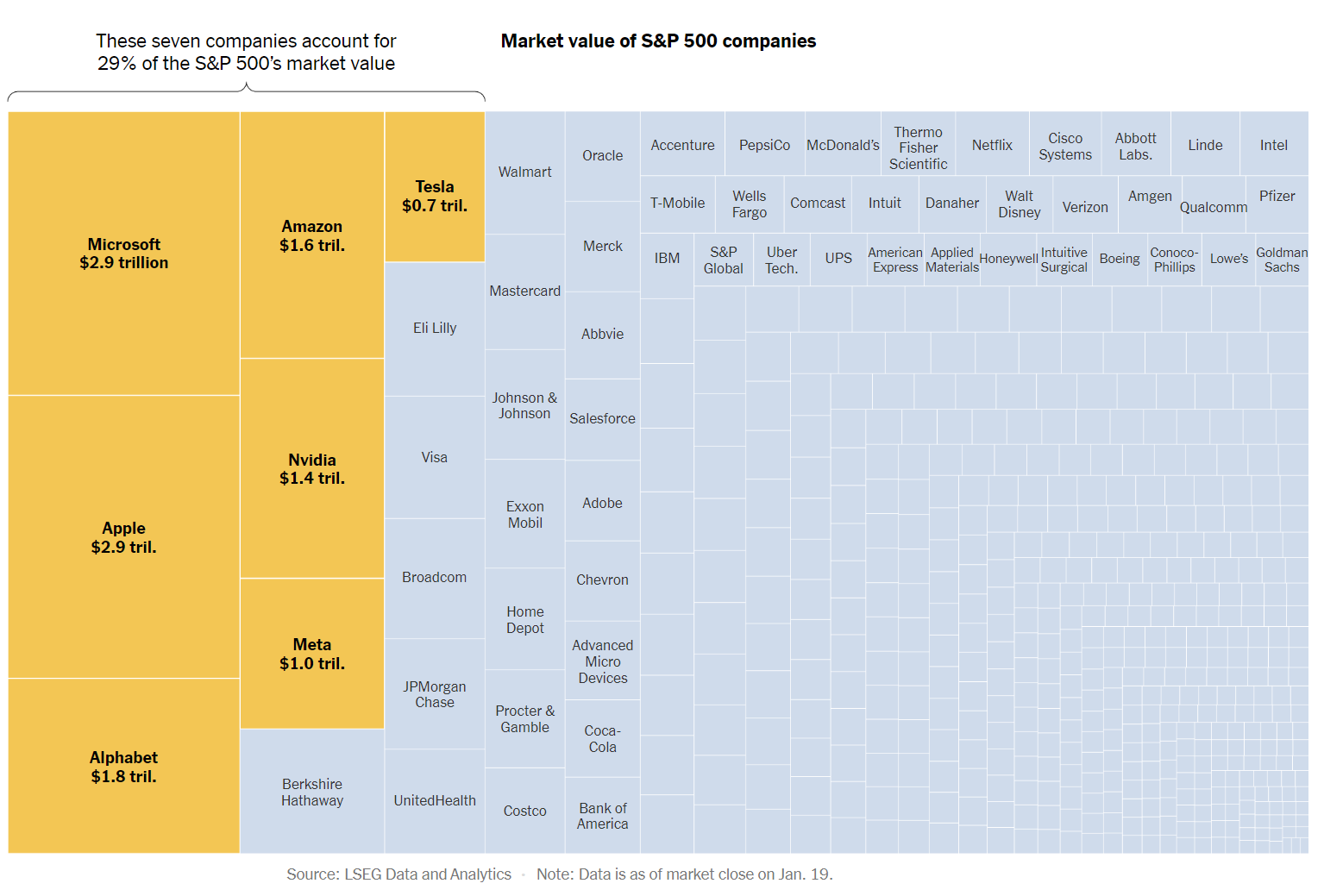
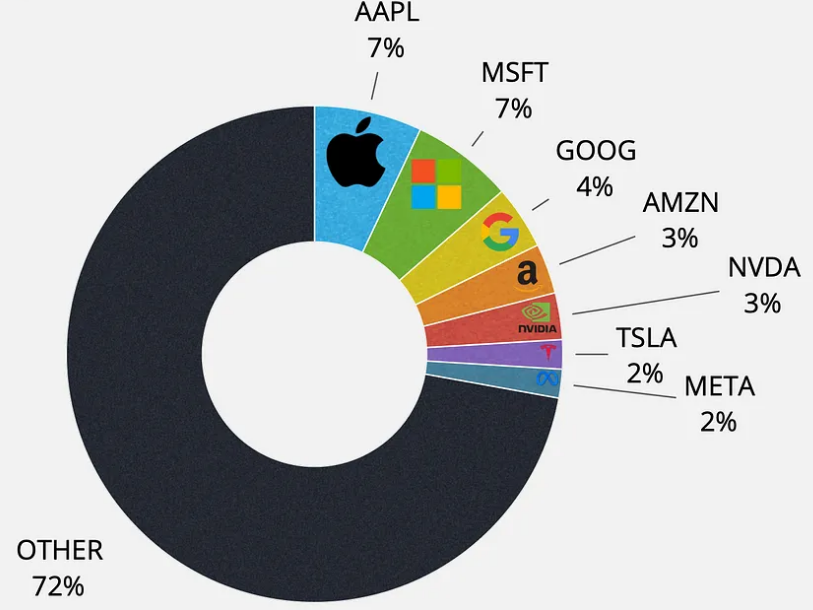
Once again, Boeing is in crisis communication mode trying to explain plane failures. Messaging could sound more authentic and compassionate.
After part of the fuselage fell off an Alaska Airlines Boeing 737 Max 9 plane, United found loose bolts needing “additional tightening” on the same model. In a flashback to the horrible deaths caused by MAX planes five years ago, the FAA grounded 171 of the planes.
On its website, Boeing lists daily “Updates,” but none of them acknowledge the fear (and of course, the inconvenience) to passengers. The audience for these messages is the public, and communications to passengers seem to be missing. One update restates what CEO Dave Calhoun said in a company-wide meeting to employees:
When it comes to the safety of our products and services, every decision and every action matters. And when serious accidents like this occur, it is critical for us to work transparently with our customers and regulators to understand and address the causes of the event, and to ensure they don’t happen again. This is and must be the focus of our team right now. I am deeply grateful to our colleagues who have been working tirelessly on our company’s response over the past two days.
We will spend time together Tuesday talking about our company’s response to this accident, and reinforcing our focus on and our commitment to safety, quality, integrity and transparency. While we’ve made progress in strengthening our safety management and quality control systems and processes in the last few years, situations like this are a reminder that we must remain focused on continuing to improve every day.
On January 9, a video of Calhoun talking with employees was posted on the site. In this message, he found some emotion, referring to the shocking pictures, which reminded him that he’s a parent and grandparent. His delivery style is natural, but much of the message sounded canned. Imagine if he said “honesty,” instead of “transparency,” which he announced like a section heading:
[Honesty.] Let me talk a little bit about what I did today and what I’ll keep doing with members of our team who are with us today. We’re going to approach this, number one, acknowledging our mistake. We are going to approach it with 100% in complete [honesty] every step of the way.”
Transparency seems best achieved through actions rather than promises—like safety.
Unfortunately for Boeing, other media sources aren’t reflecting well on the company. Several passenger TikTok videos show the missing part of the plane. (Passengers are uncharacteristically calm, perhaps because this is one of those situations when they have absolutely no control and no choice but to surrender.) A former employee whistleblower told CNBC, “It really wasn’t a surprise, sadly.”
In a CNBC interview, Corporate Communication Professor Paul Argenti criticized Boeing’s “focus on profits rather than safety, and you need to do both.” He encouraged a greater sense of urgency in [CEO Dave] Calhoun’s response: “I don’t see him saying the kinds of things that would give me confidence in the organization.” Argenti said that we need to know what went wrong and what the company will do to fix it, and “They need somebody new. . . a hero to come in and save this company.” The former CEO also struggled with communication.
Air Alaska showed a bit more compassion towards customers on the flight, but it’s at the end of the statement:
A statement from Alaska Airlines CEO, Ben Minicucci:
At Alaska Airlines, safety is our foundational value and the most important thing we focus on every day. Following tonight’s event on Flight 1282, we have decided to take the precautionary step of temporarily grounding our fleet of 65 Boeing 737-9 aircraft. Each aircraft will be returned to service only after completion of full maintenance and safety inspections. We anticipate all inspections will be completed in the next few days.
I am personally committed to doing everything we can to conduct this review in a timely and transparent way.
We are working with Boeing and regulators to understand what occurred tonight, and will share updates as more information is available. The NTSB is investigating this event and we will fully support their investigation.
My heart goes out to those who were on this flight – I am so sorry for what you experienced. I am so grateful for the response of our pilots and flight attendants. We have teams on the ground in Portland assisting passengers and are working to support guests who are traveling in the days ahead.
-Ben